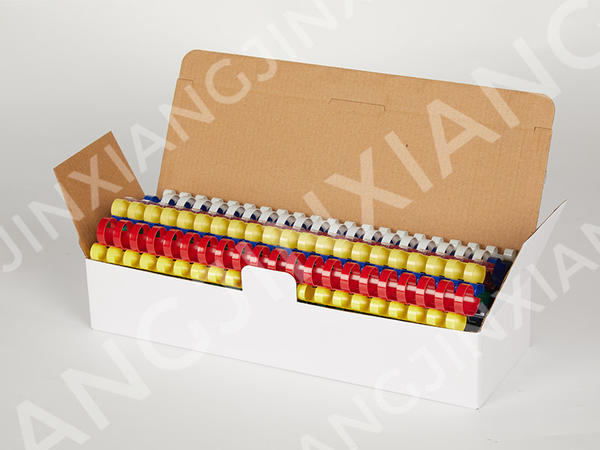
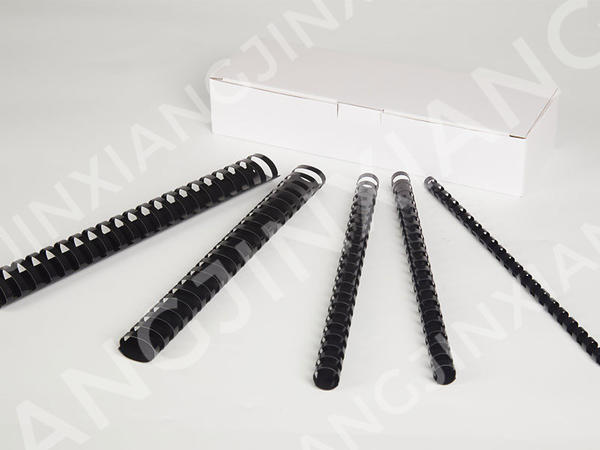
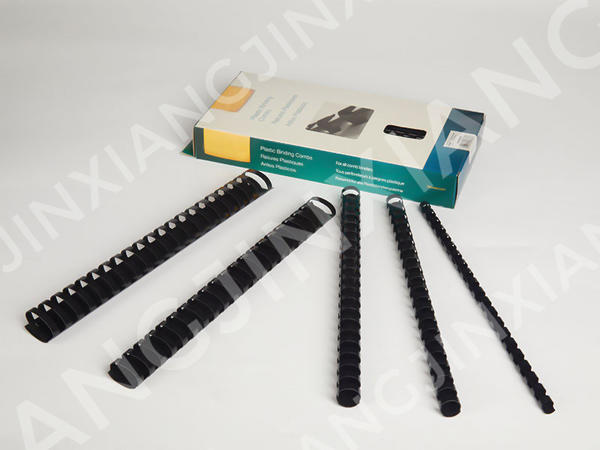
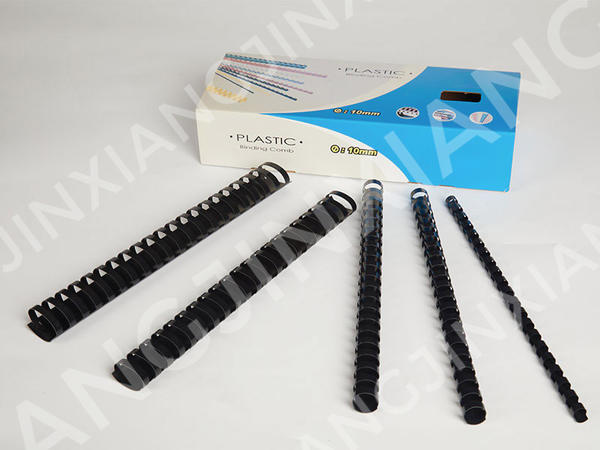
Here are some potential drawbacks or limitations to using plastic binding combs compared to other binding methods:
Limited Page Capacity: Plastic binding combs have a defined capacity determined by their diameter and number of rings. For larger documents or projects requiring substantial page counts, plastic binding combs may not be the most suitable option. When compared to coil binding or thermal binding, which offer higher page capacities and greater flexibility, users must consider the potential limitations of plastic combs. Understanding the maximum page capacity of plastic combs is crucial to avoid overloading, which can result in difficulty turning pages, compromised durability, or even damage to the binding mechanism.
Not Ideal for Permanent Binding: Plastic binding combs are ideal for documents requiring frequent updates or revisions due to their easy page insertion and removal capabilities. However, for projects necessitating a permanent binding solution, such as legal documents, policy manuals, or archival publications, plastic combs may not provide the longevity or durability required. In these instances, users may opt for more permanent binding methods like stitch binding or case binding, which offer superior durability and stability over time, ensuring the integrity of critical documents.
Limited Durability: Plastic binding combs, while cost-effective and user-friendly, may be susceptible to wear and tear, especially with heavy or rough handling. Unlike metal binding options such as wire binding or metal coil binding, plastic combs may be prone to cracking, bending, or breaking over time, compromising the structural integrity of the bound document. Users should consider the intended usage environment and handling conditions when selecting a binding method to ensure optimal durability and longevity, particularly for documents subject to frequent handling or transportation.
Not Suitable for Certain Environments: Plastic binding combs may not withstand extreme environmental conditions as effectively as other binding methods. Factors such as high temperatures, excessive humidity, or prolonged exposure to sunlight can accelerate the degradation of plastic combs, leading to brittleness, discoloration, or warping. Users operating in environments prone to temperature fluctuations or moisture exposure should explore alternative binding solutions that offer greater resistance to environmental factors, such as thermal binding or laminating, to ensure the preservation of document integrity and longevity.
Potential for Snagging: The design of plastic binding combs, featuring protruding teeth along the spine, poses a risk of pages snagging during handling or transportation. This can result in creasing, tearing, or dislodging of pages, detracting from the overall presentation quality and user experience. To mitigate this risk, users may opt for binding methods with smoother spine profiles, such as coil binding or thermal binding, which minimize the likelihood of page snagging and ensure a seamless reading experience, particularly for documents subject to frequent reference or circulation.
Less Versatile Finishing Options: Plastic binding combs offer limited opportunities for customization and finishing compared to other binding methods. While certain enhancements such as cover customization or imprinting are feasible with plastic combs, options such as foil stamping, embossing, or debossing may be more challenging to execute effectively. Users seeking elaborate branding or decorative elements may find alternative binding methods like case binding or saddle stitching better suited to their requirements, as they offer greater flexibility in finishing options and aesthetic enhancements, elevating the overall presentation quality and visual impact of the bound document.
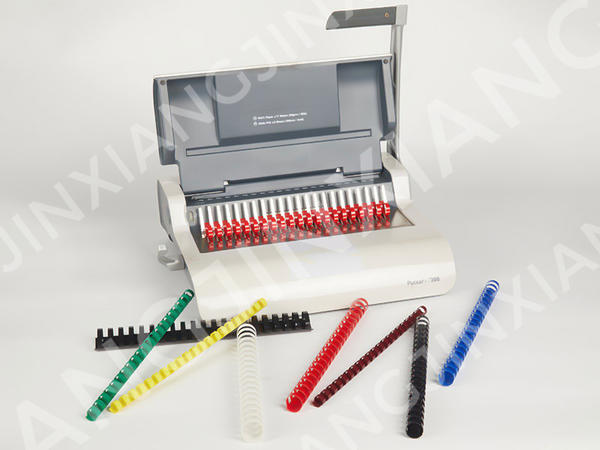
Multi-Color and Various Size Plastic Binding Comb 84 Holes-Plastic Binding Combs/Rings
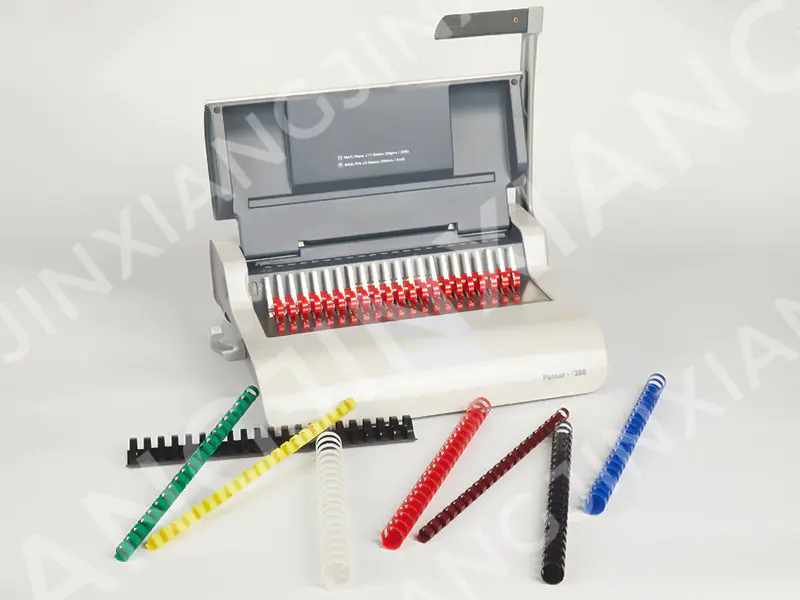

Multi-Color and Various Size Plastic Binding Comb 84 Holes-Plastic Binding Combs/Rings





 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español